AMRES Infrastructure
AMRES infrastructure is the scientific-research and education computer network of the Republic of Serbia in functional and technical terms, together with external links which connect it with the environment (Internet, GÉANT, other providers, etc.) and server-computer infrastructure. It includes all devices owned or leased by AMRES and all telecommunication links owned or leased by AMRES from telecommunication providers.
Network part of AMRES infrastructure consists of access network, network backbone and external links.
Access Network links AMRES users to points of presence (PoP) of AMRES infrastructure. AMRES PoPis every location of AMRES infrastructure containing communication devices that link minimum two other AMRES users.
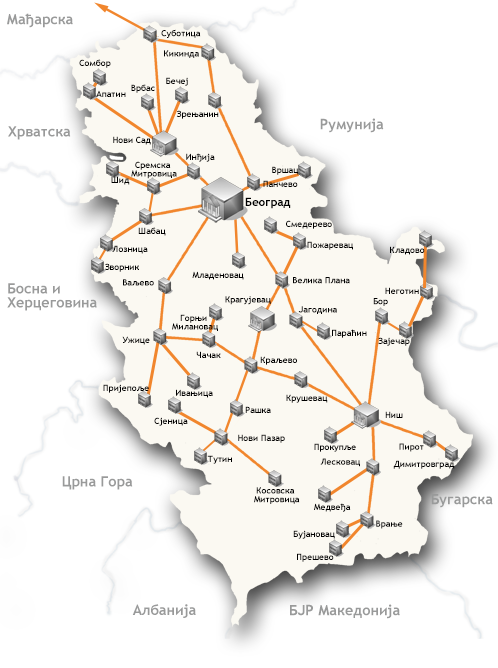
Network Backbone consists of inter-city and city optical links which connect AMRESPoP locations. In current active network topology of AMRES infrastructure, AMRES PoPs are located in 50 cities: Belgrade, Novi Sad, Niš, Kragujevac, Subotica, Kikinda, Zrenjanin, Vršac, Pančevo, Sombor, Apatin, Vrbas, Bečej, Inđija, Ruma, Šid, Semska Mitrovica, Šabac, Loznica, Valjevo, Užice, Prijepolje, Ivanjica, Čačak, Kraljevo, Kruševac, Jagodina, Velika Plana, Mladenovac, Smederevo, Požarevac, Paraćin, Gornji Milanovac, Leskovac, Prokuplje, Vranje, Medveđa, Bujanovac, Preševo, Bor, Zaječar, Negotin, Kladovo, Pirot, Dimitrovgrad, Novi Pazar, Raška, Sjenica, Tutin and Kosovska Mitrovica.
External Links are links of AMRES infrastructure with GÉANT network, academic networks of other countries, telecommunication service providers and other partner institutions.
Technologies used in AMRES infrastructure depend on the type and intended purpose of the link itself:
- Optical technologies are used for data transfer via optical cable infrastructure (dark fiber). AMRES has 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GBASE-X) and Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-X) both in the backbone and in the access network. Various characteristics of optical 10 Gigabit Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet modules are used, which depend on the length of optical link and the type of optical cable (singlemode and multimode),
- Other access technologies (e.g. xDSL VPN) performed in cooperation with some of local telecommunication providers which make data transfer from AMRES users to AMRES PoPs.

